Recursion
Recursion
Definition:
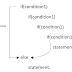
A function containing either a call statement to
itself or a call statement to another function that may result in a call
statement back to the original function , this type of function is known as
recursive function(the procedure is called recursion).
Well defined recursive function:
In order that a program should not indefinitely a recursive
function must have the following properties…
- There must be certain criteria, known as base criteria. For which the function doesn’t call itself.
- Each time the function does call itself, either directly or indirectly and it must be closer to base criteria.
A recursive function with this two properties is said to be
well defined.
Principles of recursive function:
For implementing and designing the good recursive program we
must make certain assumption like
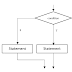
- Base case: it is the terminating condition for the problem while designing any recursive algorithm, we must choose a proper terminating condition for the problem.
- If condition: It provides the terminating criteria.
- Every time a new recursive call is made, a new memory space is allocated to each automatic variable used by the recursive routine.
- Each time recursive call is there, the duplicates values of the local variables of the recursive call are pushed into the stack, within respective call & all these values are available to the respective function, call when it is popped of from the stack.
- Recursive case: generally, else part of the recursive definitions calls the functions recursively.
Disadvantages of recursion:
- It consumes more storage space because the recursive calls along with the automatic variables are stored on the stack.
- The computer may run out of memory if the recursive calls are not checked.
- It is not more efficient I terms of speed & execution time.
- If proper precautions are not taken, recursive may result in non terminating functions.
- In recursion we can’t implement the concept of looping.




No comments